Page 20 - Echoes of the Global South V2
P. 20
d. Natural Capital
Natural capital in the Global South includes the stock of environmental resources such as forests, water, minerals,
biodiversity, and clean air – all playing a crucial role in the region’s economic growth and development. Given the
significant population density of the region, these resources also face significant pressures from rapid population
growth, urbanisation, and industrial expansion. Many countries are also experiencing high rates of deforestation, land
degradation, overfishing, water scarcity, and biodiversity loss due to unsustainable extraction, poor governance, and
weak environmental regulations, with climate change further exacerbating these challenges and leading to increased
frequency and severity of extreme weather events that disproportionately affect the most vulnerable communities
and economies. 45,46,47
While there are prospects for environmental and ecological sustainability through the adoption of green technologies,
sustainable agricultural practices, and renewable energy sources, many countries in the Global South face
constraints related to limited financial resources, technological capacity, and institutional frameworks to implement
such measures effectively. The implications of the current state of natural capital are profound; unsustainable use of
resources threatens food and water security, exacerbates poverty and inequality, and undermines long-term economic
stability and growth. However, if managed sustainably, natural capital can become a source of resilience, economic
diversification, and inclusive development by fostering sectors such as eco-tourism, sustainable agriculture, and clean
48
energy. For this to happen, countries in the Global South need to strengthen environmental governance, enforce
regulations, invest in sustainable infrastructure, and adopt inclusive policies that balance economic development with
preserving natural ecosystems.
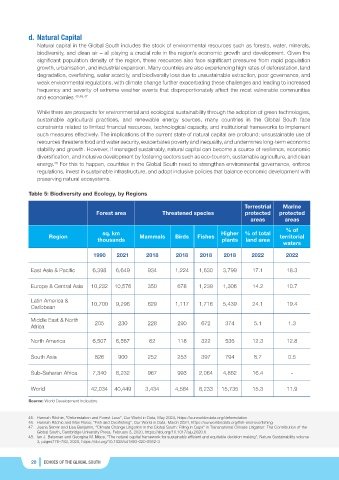
Table 5: Biodiversity and Ecology, by Regions
Terrestrial Marine
Forest area Threatened species protected protected
areas areas
% of
sq. km Higher % of total
Region Mammals Birds Fishes territorial
thousands plants land area
waters
1990 2021 2018 2018 2018 2018 2022 2022
East Asia & Pacific 6,398 6,649 934 1,224 1,630 3,799 17.1 18.3
Europe & Central Asia 10,232 10,576 350 678 1,239 1,306 14.2 10.7
Latin America & 10,700 9,296 629 1,117 1,716 5,439 24.1 19.4
Caribbean
Middle East & North 205 230 228 290 672 374 5.1 1.3
Africa
North America 6,507 6,567 62 118 322 536 12.3 12.8
South Asia 826 900 252 253 397 794 8.7 0.5
Sub-Saharan Africa 7,340 6,232 967 993 2,064 4,862 16.4 -
World 42,034 40,449 3,434 4,584 8,233 15,735 15.3 11.9
Source: World Development Indicators
45. Hannah Ritchie, “Deforestation and Forest Loss”, Our World in Data, May 2024, https://ourworldindata.org/deforestation
46. Hannah Ritchie and Max Roser, “Fish and Overfishing”, Our World in Data, March 2024, https://ourworldindata.org/fish-and-overfishing
47. Joana Setzer and Lisa Benjamin, “Climate Change Litigation in the Global South: Filling in Gaps” in Transnational Climate Litigation: The Contribution of the
Global South, Cambridge University Press, February 3, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1017/aju.2020.6
48. Ian J. Bateman and Georgina M. Mace, “The natural capital framework for sustainably efficient and equitable decision making”, Nature Sustainability volume
3, pages776–783, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-020-0552-3
20 ECHOES OF THE GLOBAL SOUTH