Page 28 - Echoes of the Global South V2
P. 28
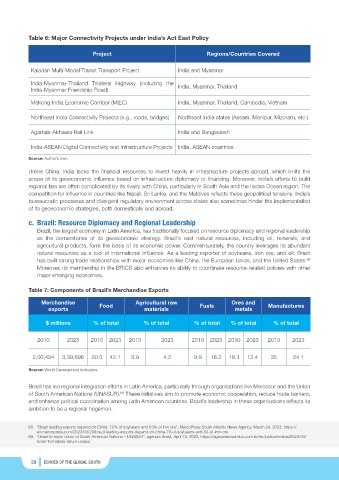
Table 6: Major Connectivity Projects under India’s Act East Policy
Project Regions/Countries Covered
Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project India and Myanmar
India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway (including the India, Myanmar, Thailand
India-Myanmar Friendship Road)
Mekong-India Economic Corridor (MIEC) India, Myanmar, Thailand, Cambodia, Vietnam
Northeast India Connectivity Projects (e.g., roads, bridges) Northeast India states (Assam, Manipur, Mizoram, etc.)
Agartala-Akhaura Rail Link India and Bangladesh
India-ASEAN Digital Connectivity and Infrastructure Projects India, ASEAN countries
Source: Author’s own
Unlike China, India lacks the financial resources to invest heavily in infrastructure projects abroad, which limits the
scope of its geoeconomic influence based on infrastructure diplomacy or financing. Moreover, India’s efforts to build
regional ties are often complicated by its rivalry with China, particularly in South Asia and the Indian Ocean region. The
competition for influence in countries like Nepal, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives reflects these geopolitical tensions. India’s
bureaucratic processes and divergent regulatory environment across states also sometimes hinder the implementation
of its geoeconomic strategies, both domestically and abroad.
c. Brazil: Resource Diplomacy and Regional Leadership
Brazil, the largest economy in Latin America, has traditionally focused on resource diplomacy and regional leadership
as the cornerstones of its geoeconomic strategy. Brazil’s vast natural resources, including oil, minerals, and
agricultural products, form the basis of its economic power. Commensurately, the country leverages its abundant
natural resources as a tool of international influence. As a leading exporter of soybeans, iron ore, and oil, Brazil
68
has built strong trade relationships with major economies like China, the European Union, and the United States.
Moreover, its membership in the BRICS also enhances its ability to coordinate resource-related policies with other
major emerging economies.
Table 7: Components of Brazil’s Merchandise Exports
Merchandise Agricultural raw Ores and
exports Food materials Fuels metals Manufactures
$ millions % of total % of total % of total % of total % of total
2010 2023 2010 2023 2010 2023 2010 2023 2010 2023 2010 2023
2,00,434 3,39,696 30.3 42.1 3.9 4.2 9.9 16.2 18.1 12.4 35 24.1
Source: World Development Indicators
Brazil has led regional integration efforts in Latin America, particularly through organisations like Mercosur and the Union
of South American Nations (UNASUR). These initiatives aim to promote economic cooperation, reduce trade barriers,
69
and enhance political coordination among Latin American countries. Brazil’s leadership in these organisations reflects its
ambition to be a regional hegemon.
68. “Brazil leading exports depend on China: 70% of soybeans and 63% of iron ore”, MercoPress South Atlantic News Agency, March 29, 2023, https://
en.mercopress.com/2023/03/29/brazil-leading-exports-depend-on-china-70-of-soybeans-and-63-of-iron-ore
69. “Brazil to rejoin Union of South American Nations – UNASUR”, agencia Brasil, April 10, 2023, https://agenciabrasil.ebc.com.br/en/justica/noticia/2023-04/
brazil-formalizes-return-unasur
28 ECHOES OF THE GLOBAL SOUTH